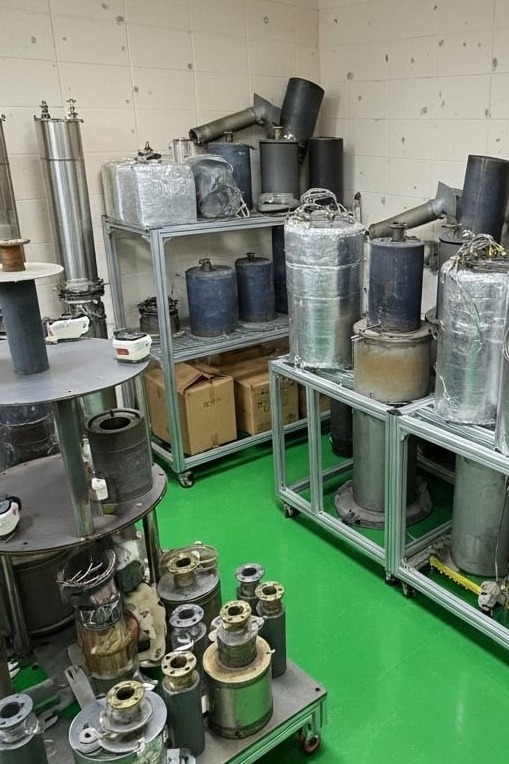
DR FuelCell Technology Division
DR FuelCell is a hydrogen generator specialist with the widest range of fuel compatibility and integrated solutions compared to competitors. Our core technological capabilities consist of five key areas: multi-fuel compatibility, proprietary catalyst development, integrated reactor design, enhanced safety, and CO₂ utilization technology.
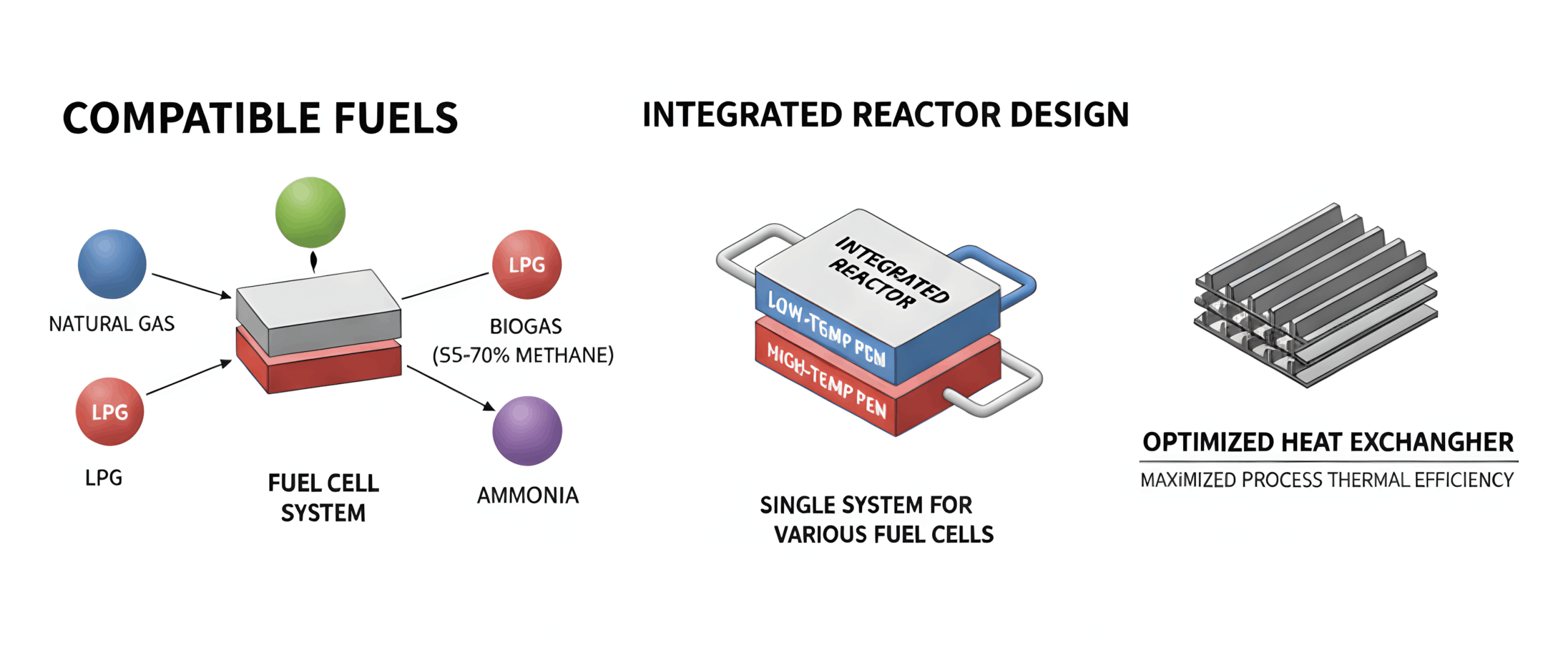
Multi-fuel compatibility technology is a differentiated capability that enables processing of various fuel sources—including natural gas, LPG, biogas, ammonia, and e-methanol—on a single platform. It is compatible with all fuel cell systems including low-temperature and high-temperature PEMFC and SOFC, with automatic fuel recognition and optimal operation mode switching. Unlike competitors who specialize in specific fuels, this represents our core competitive advantage in flexibly responding to market changes.
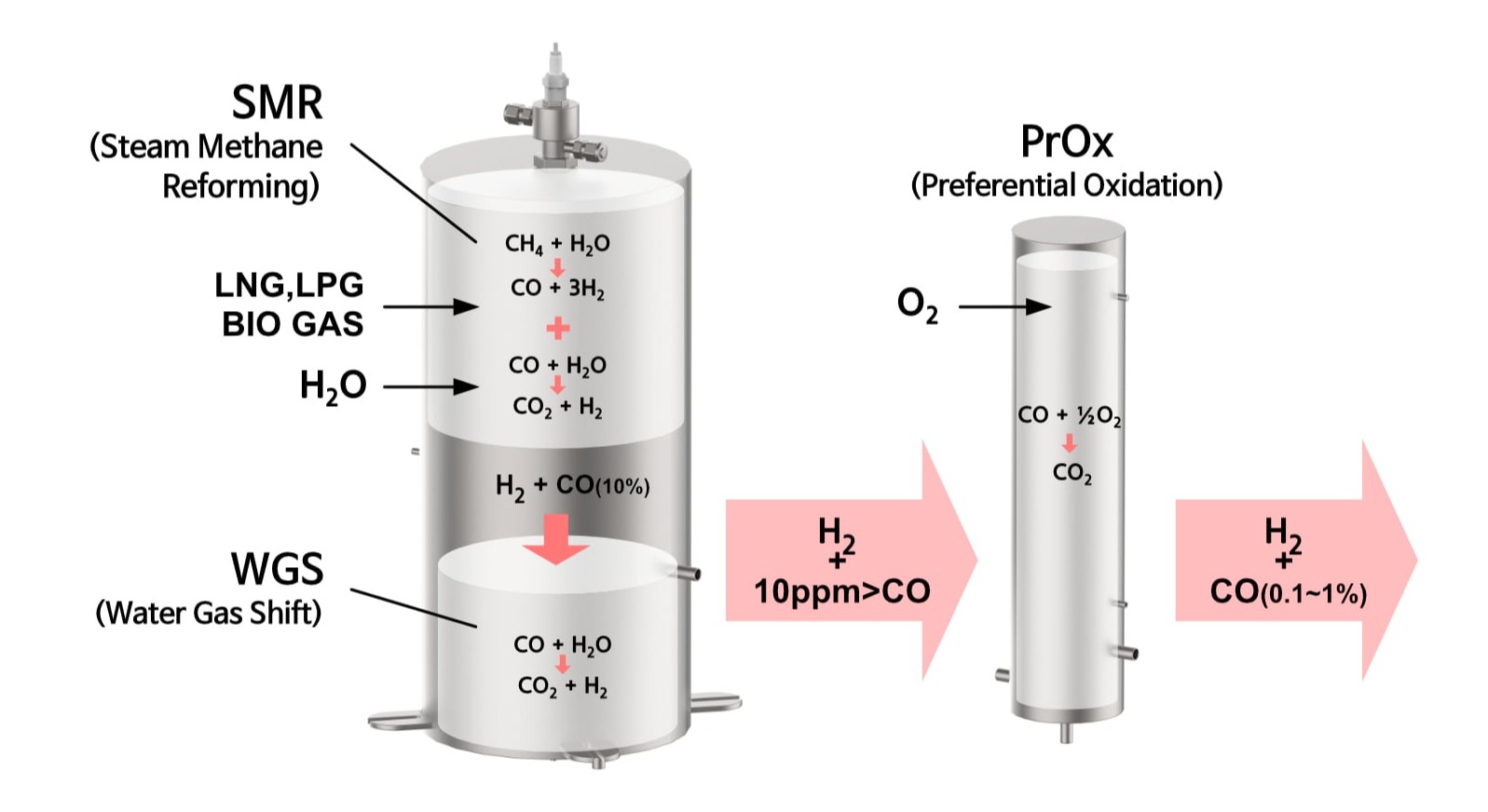
Integrated reactor design technology implements compact systems by optimizing steam reforming and autothermal reforming reactions. Energy efficiency is maximized through heat exchanger optimization, and Balance of Plant (BOP) integration enables seamless operation with fuel cell systems.
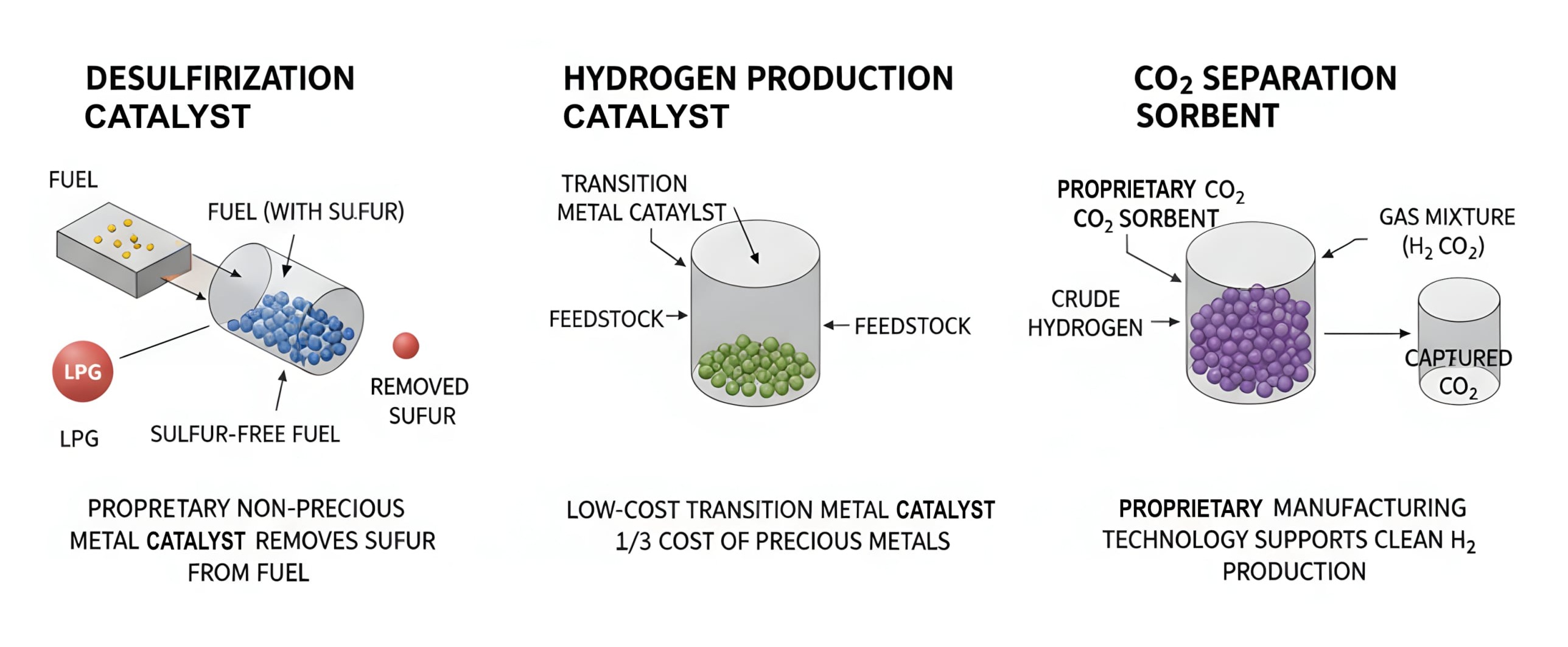
Additionally, we produce high-purity hydrogen (99.99% or higher) by reducing CO concentration to below 10 ppm through Water Gas Shift reactors. Our proprietary catalyst technology is the core of our cost competitiveness—we have developed transition metal catalysts for desulfurization and hydrogen production in-house, minimizing dependence on expensive precious metal catalysts. Our Ru-based catalysts for ammonia cracking achieve over 99% decomposition efficiency, and we possess both sphere-type and monolith-type catalyst technologies.
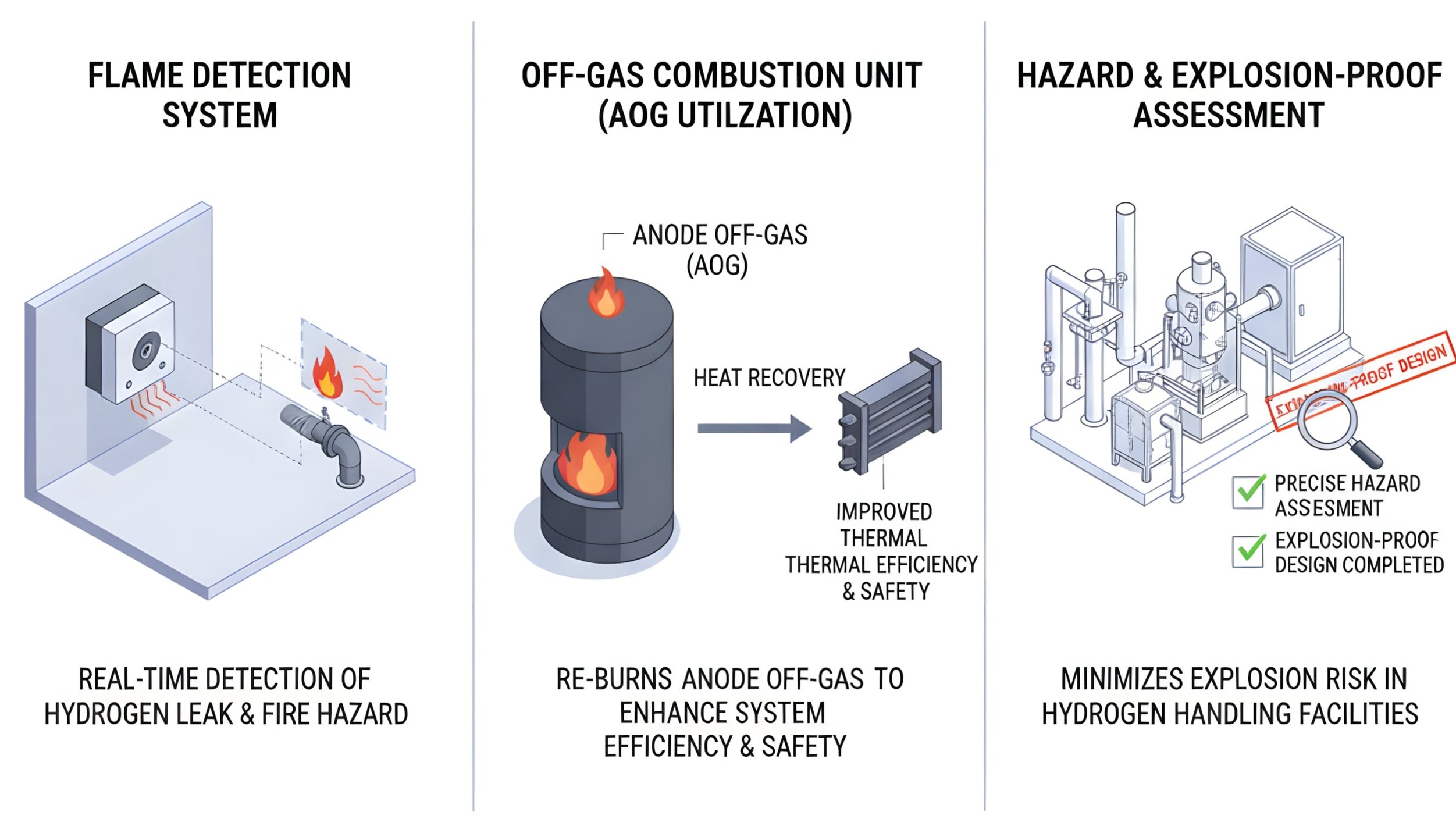
CO₂ utilization technology is key to achieving carbon neutrality. We possess carbon dioxide separation and capture technology and are developing turquoise hydrogen production technology. We are researching technology to simultaneously produce hydrogen and high-value carbon materials without CO₂ emissions through methane pyrolysis. These technologies work complementarily to provide an end-to-end solution from fuel input to high-purity hydrogen production and fuel cell power generation.